IPO Process in India
As an investor, you must have endeavored to find a suitable opportunity for investing in Upcoming IPOs. But do you know about the initial public offering process? Well, knowing about the IPO process in India will certainly enhance your knowledge. Read on to know more.
Understanding The Need For IPO Process
A company can change itself from a privately-held body to a publicly-traded entity through the process of Initial Public Offering (IPO). Typically, companies offer IPO to raise money and get access to liquidity by offering their stocks/shares to the public. Companies have to abide by the IPO process in India - as stipulated by stock exchanges - before its shares are eligible to be publicly traded. This process is often complicated and long-drawn.
You Might Also Like, What is IPO?
Understanding The Need For IPO Process
A company can change itself from a privately-held body to a publicly-traded entity through the process of Initial Public Offering (IPO). Typically, companies offer IPO to raise money and get access to liquidity by offering their stocks/shares to the public. Companies have to abide by the IPO process in India - as stipulated by stock exchanges - before its shares are eligible to be publicly traded. This process is often complicated and long-drawn.
You Might Also Like, What is IPO?
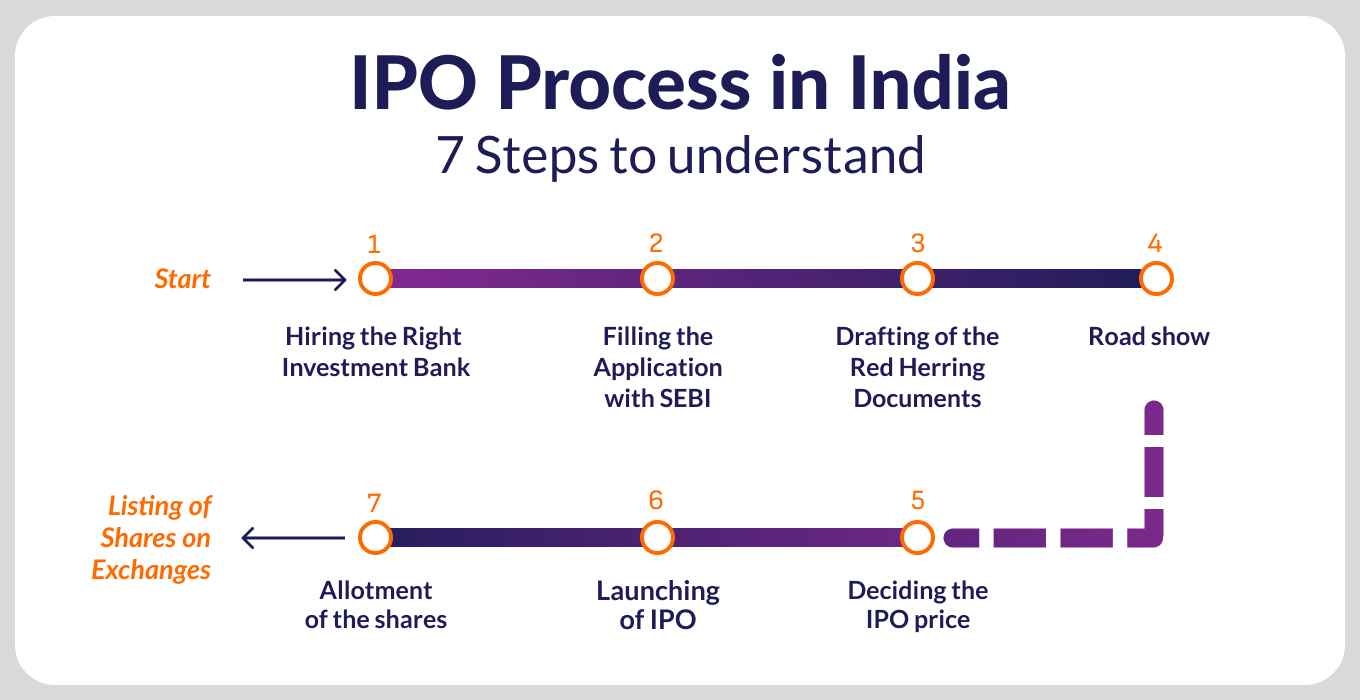
IPO Process Steps:
Step 1: Hiring Of An Underwriter Or Investment Bank
To start the initial public offering process, the company will take the help of financial experts, like investment banks. The underwriters assure the company about the capital being raised and act as intermediaries between the company and its investors. The experts will also study the crucial financial parameters of the company and sign an underwriting agreement. The underwriting agreement will usually have the following components:
- Details of the deal
- Amount to be raised
- Details of securities being issued
Step 2: Registration For IPO
This IPO step involves the preparation of a registration statement along with the draft prospectus, also known as Red Herring Prospectus (RHP). Submission of RHP is mandatory, as per the Companies Act. This document comprises all the compulsory disclosures as per the SEBI and Companies Act. Here’s a look at the key components of RHP:
- Definitions: It contains the definitions of the industry-specific terms.
- Risk Factors: This section discloses the possibilities that could impact a company’s finances.
- Use of Proceeds: This section discloses how the money raised from investors will be used.
- Industry Description: This section details the working of the company in the overall industry segment. For instance, if the company belongs to the IT segment, the section will provide forecasts and predictions about the segment.
- Business Description: This section will detail the core business activities of the company.
- Management: This section provides information about key management personnel.
- Financial Description: This section comprises financial statements along with the auditor's report.
- Legal and Other Information: This section details the litigation against the company along with miscellaneous information.
This document has to be submitted to the registrar of companies, three days before the offer opens to the public for bidding. Alongside, the submitted registration statement has to be compliant with the SEC rules. Post-submission, the company can make an application for an IPO to SEBI.
Step 3: Verification by SEBI:
Market regulator, SEBI then verifies the disclosure of facts by the company. If the application is approved, the company can announce a date for its IPO.
Step 4: Making An Application To The Stock Exchange
The company now has to make an application to the stock exchange for floating its initial issue.
Step 5: Creating a Buzz By Roadshows
Before an IPO opens to the public, the company endeavors to create a buzz in the market by roadshows. Over a period of two weeks, the executives and staff of the company will advertise the impending IPO across the country. This is basically a marketing and advertising tactic to attract potential investors. The key highlights of the company are shared with various people, including business analysts and fund managers. The executives adopt various user-friendly measures, like Question and Answer sessions, multimedia presentations, group meetings, online virtual roadshows, and so on.
Step 6: Pricing of IPO
The company can now initiate pricing of IPO either through Fixed Price IPO or by Book Binding Offering. In the case of Fixed Price Offering, the price of the company’s stocks is announced in advance. In the event of Book Binding Offering, a price range of 20% is announced, following which investors can place their bids within the price bracket. For the bidding process, the investors have to place their bids as per the company’s quoted Lot price, which is the minimum number of shares to be purchased. Alongside, the company also provides for IPO Floor Price, which is the minimum bid price and IPO Cap Price, which is the highest bidding price. The booking is typically open from three to five working days and investors can avail the opportunity of revising their bids within the stipulated time. After completion of the bidding process, the company will determine the Cut-Off price, which is the final price at which the issue will be sold.
Step 7: Allotment of Shares
Once the IPO price is finalised, the company along with the underwriters will determine the number of shares to be allotted to each investor. In the case of over-subscription, partial allotments will be made. The IPO stocks are usually allotted to the bidders within 10 working days of the last bidding date.
Also Read, IPO Allotment Process
Other Factors That The Company Consider Before The Initial Public Offering Process Is Complete:Yes, any company will endeavour to prevent company insiders or internal investors from participating in the IPO process. Remember, company insiders trading in their own shares can disrupt the demand and supply balance. Not only does this measure protect retail investors from manipulated offer prices but also prevents fraudulent company officials to fob off overpriced stocks at the expense of general investors. This measure also helps to fend off additional selling pressure from inside, and thus sustain the market price of shares.
Conclusion
Now that you know the IPO process steps and its importance, you can make informed decisions to invest in IPOs. Also, have a look at Indiainfoline upcoming IPO calendar to aid your understanding on IPO. To make prudent investment decisions, you will be invariably required to do a lot of legwork. This includes selecting a trusted and reliable financial partner. You must select a stockbroking firm providing multiple benefits such as smooth trading platforms, an all-in-one account to trade in all investment options, zero Demat account opening and AMC charges, award-winning research, and so on.
