5 May 2025 , 12:58 PM
Bank Credit Falls Sharply:
India’s pace of banking credit has been moderating. As per the latest data from RBI, year-on-year credit growth has fallen from 10.9% as on the beginning of April to 10.3% now. The moderation is despite Reserve Bank of India’s recently announced repo rate cuts and suggests growing caution in Lending.
As per RBI’s latest data release, credit growth dipped sharply in April. From 10.9% YoY growth at the beginning of April, it has fallen to 10.3%. The falling credit growth has happened despite RBI utilising its key policy tool to increase lending. RBI had lowered repo rate by 50bps in the recent past.
On the one hand, moderation in credit growth represents a significant change from the excessively hot conditions seen over the last year. During 2024, banking credit had jumped 20% on a year-on-year basis, supported by strong demand from corporates, retail borrowers as well as from services sector. The high pace was unsustainable and carries risks of asset quality deterioration and overheating in pockets of the economy.
However, the sharp fall in credit growth, is increasingly a cause for worry. At 10.3%, banking credit expanded at the slowest pace in three years. A slowdown in both retail and corporate credit is likely resulting in the slowdown. A variety of factors including tighter norms for NBFC credit and unsecured retail credit (credit cards, personal loans etc) are being attributed to.
Figure: Credit Growth dips to a 3 year low
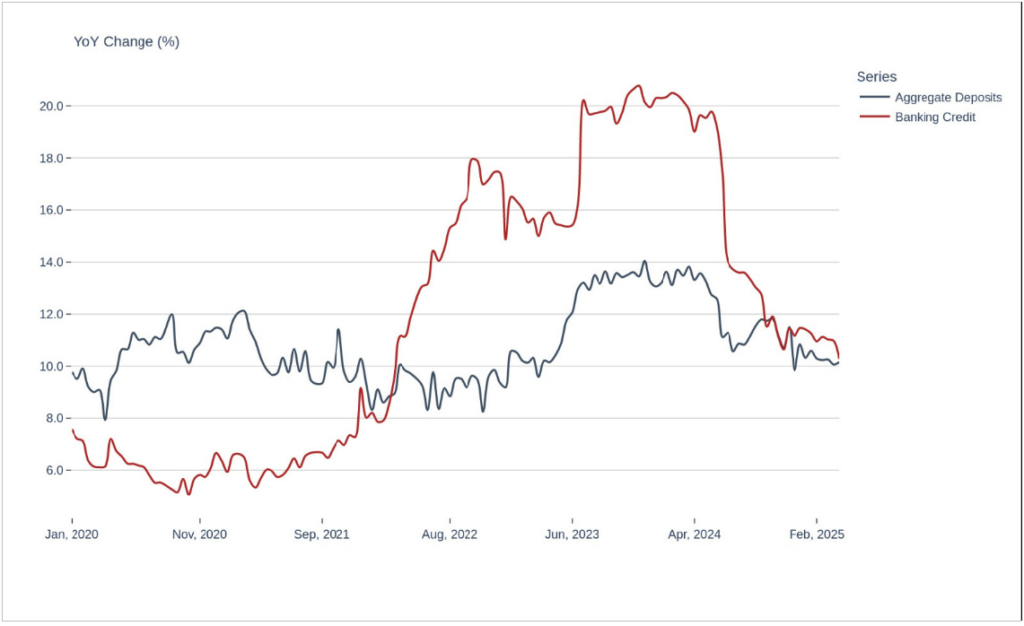
Source: RBI
RBI’s Repo Rate Cut: A Strategic Move to Stimulate Economic Growth
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) cut its benchmark policy interest rate (repo rate) by 0.25% points to 6.00% in April 2025. It is the second rate cut in 2025 year and takes the total cut to 50 basis points. The move signals a shift in RBI’s monetary policy from ‘Neutral’ to ‘Accomodative’. In light of slowing credit growth and macroeconomic uncertainties, RBI has been proactive with its policy tools to offer support.
Figure: Repo Rate is coming off and policy stance is turning accommodative
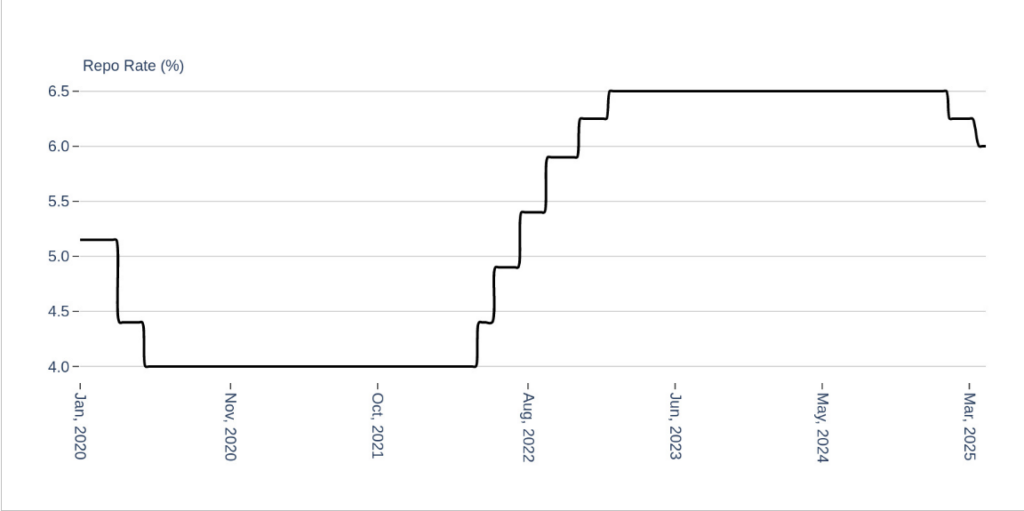
Source: RBI
What is Repo Rate – A Primer
The repo rate is the rate at which the RBI lends to commercial banks. A lower rate of interest reduces the cost of borrowing for banks, and can ultimately mean lower interest rates for loans to consumers and businesses. It is the primary device employed by the RBI to manage the economic activity in the country.
Goals behind a cut in the Repo Rate
Encouraging Credit Demand: By making borrowing cheaper, it encourages households, firms to borrow and spend on consumption and investment goods. That can be particularly good for rate sensitive areas like housing, auto and small business.
Boosting The Economy: Economists say Reserve Bank of India’s cut will help lift economic activity by bringing down the cost of spending and investment.
Inflation Management: The RBI’s move to reduce the repo rate comes against the backdrop of inflation moderating particularly in food prices. Retail inflation dropped, giving the central bank a room to have a more accommodative stance without actually contravening its inflation targets.
Boost Liquidity: The rate reduction is combined with steps to provide liquidity to the banking system so banks have the required cash to lend more money.
The SDF: RBI’s Passive Liquidity Absorber
The SDF is a non-collateralised instrument which the banks can use for parking their surplus funds at the RBI and earn interest at a slightly lower rate than the repo. It was implemented in April 2022 as a cleaner and more efficient alternative to the conventional reverse repo.
Unlike reverse repo, the SDF does not mandate the RBI to transfer government securities as collateral, making it a more efficient tool to absorb liquidity. This has now become the de-facto floor of the RBI’s LAF corridor.
SDF Balances Ease After The Spike In April
A rapid acceleration in the RBI’s daily SDF started in April 2025. 20D average SDF utilization has increased to nearly INR 2 trn – a high not seen since 2022. This rise resulted in overall liquidity conditions tightening after the improving conditions witnessed during the early part of 2025. As per latest release, SDF balances have moderated. This is likely to improve liquidity as it has been a key liquidity absorber in the recent past.
Figure: SDF utilization moderates after the spike
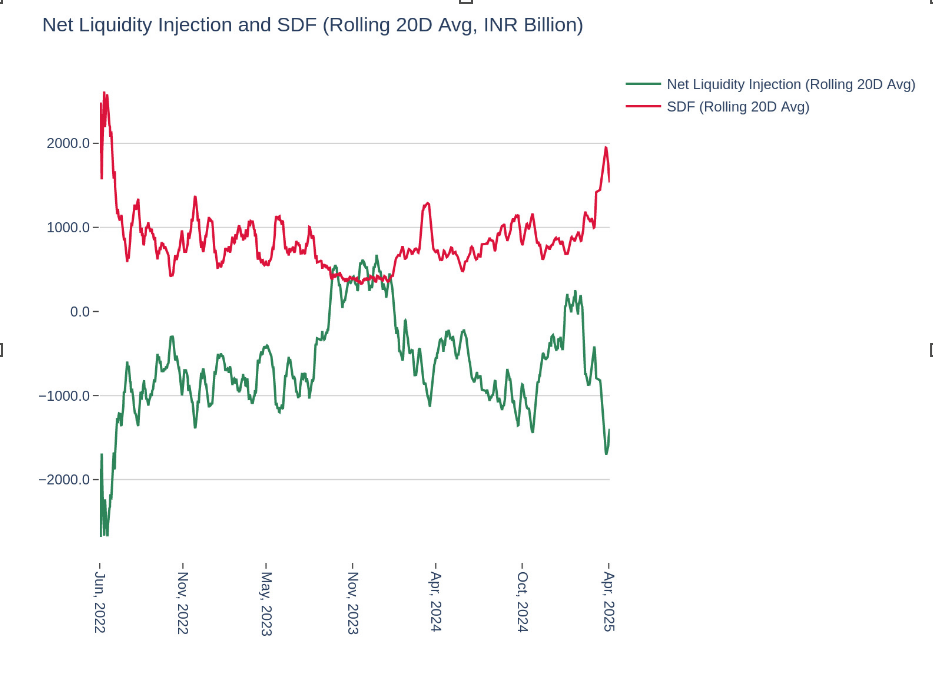
Source: RBI
Credit Deposit Ratio eased even as Liquidity Remained tight
In the recent past, Indian banking witnessed high credit growth and rising credit deposit ratio. This had also resulted in tighter liquidity conditions, higher competition for funding and higher funding costs.
As per latest RBI data, CDR has moderated from its recent peak to around 78%. A moderating CDR indicates either the relative pace of credit slowed or deposits picked up or a combination of both happened. A closer look at the net liquidity in the system indicates that the banks parked excess funds in low interest earnings SDF facilities as the demand for credit moderated. Despite the obvious ramification that credit growth might be slowing, a balanced and/or moderate CDR provides operational room to the banks in the event of a pickup in credit growth.
Figure: Banking Credit Deposit Ratio Drops – Improving Liquidity or Moderating Credit?
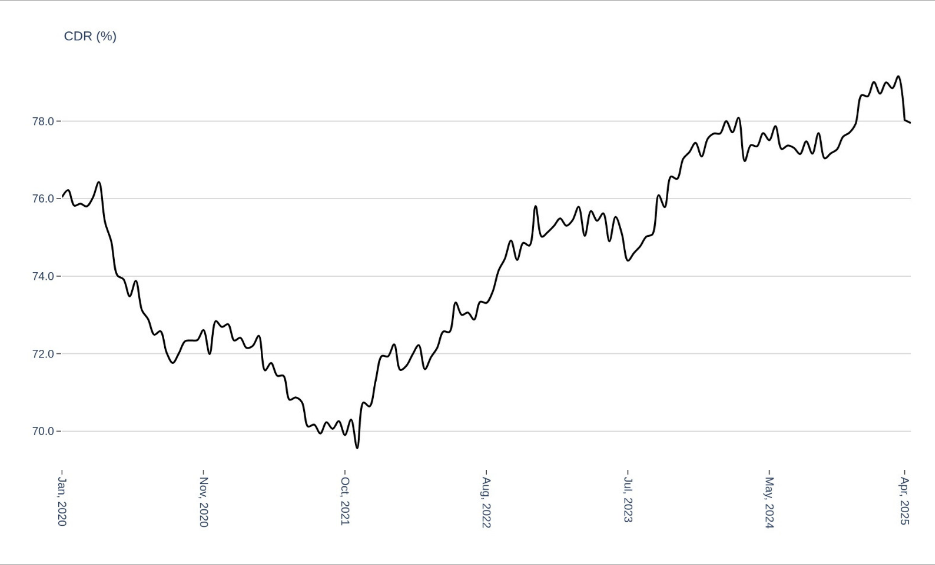
Source: RBI
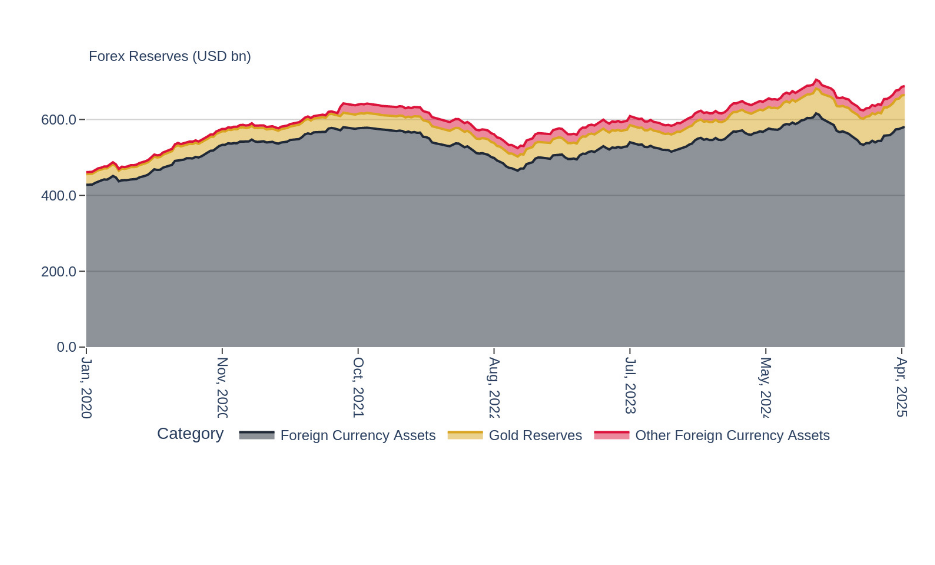
Forex Reserves Are Rising Again
India’s forex reserves increased by USD 2.2 bn and hit a six-month high of USD688.1 bn for the week ending April 25, 2025. Gold Reserves dropped marginally by USD 207 m. However, the rise in foreign currency assets more than compensated for it. Since January low, forex reserves have improved by USD 64 bn. Gold was a significant contributor to the increase. While gold only accounts for 12% of total reserves, it contributed to 25% of these incremental reserves. After having seen significant depletion during the later part of 2024, forex reserves are now close to their peak.
Figure: India’s Forex Reserves Are Nearing The Previous Peak
 Source: RBI
Source: RBI
Related Tags

![]() IIFL Customer Care Number
IIFL Customer Care Number
(Gold/NCD/NBFC/Insurance/NPS)
1860-267-3000 / 7039-050-000
![]() IIFL Capital Services Support WhatsApp Number
IIFL Capital Services Support WhatsApp Number
+91 9892691696
IIFL Capital Services Limited - Stock Broker SEBI Regn. No: INZ000164132, PMS SEBI Regn. No: INP000002213,IA SEBI Regn. No: INA000000623, SEBI RA Regn. No: INH000000248, DP SEBI Reg. No. IN-DP-185-2016, BSE Enlistment Number (RA): 5016
ARN NO : 47791 (AMFI Registered Mutual Fund & Specialized Investment Fund Distributor), PFRDA Reg. No. PoP 20092018

This Certificate Demonstrates That IIFL As An Organization Has Defined And Put In Place Best-Practice Information Security Processes.