A share represents a unit of equity ownership in a company. Shareholders are entitled to any profits that the company may earn in the form of dividends. They are also the bearers of any losses that the company may face. In simple words, if you are a shareholder of a company, you hold a percentage of ownership of the issuing company in proportion to the shares you have bought, often managed through a share market app. Keep reading to acquire more details about various share types.
How Do Shares Work in the Share Market?
To understand how shares work, it is vital to obtain a clear notion first about what are shares:
What do shares mean?
A share signifies part-ownership in a firm. When someone buys a share in a firm, they now own a part of that company. Over time, if the firm works well, the share value improves and the person who has shares in the company will reap the benefits—through profits in the form of dividends.
Trading refers to shares being listed, after which investors can buy and sell them. This describes how the share market works. It’s crucial to remember that the price of these shares can change every day because of changes in the market, demand and supply, or even how well the firm is doing.
How does a firm issue shares?
There is a fairly clear step-by-step method for a firm to issue shares:
- Draughting a Prospectus: The first step for the company is to write a prospectus, which is also called the Draft Red Herring Prospectus (DRHP), and send it to the SEBI for assessment.
- SEBI clearance: Once this prospectus is presented to the SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India), if they are satisfied, they send it along for clearance.
- Apply to Stock Exchanges: After getting the green light, the company starts applying to stock exchanges like BSE (Bombay Stock Exchange) or NSE (National Stock Exchange). These exchanges carefully look over the applications and then give their approval.
- Set Price: The firm sets a price for its shares, and for a few days, the Initial Pubic Offering (IPO) is open to the public so that investors can apply for them.
- Allotment of Shares: This is when the corporation looks over the applications from investors and decides who to provide shares to based on how many people want them.
- Listing on the Stock Exchange: With the last formalities complete, the shares are formally listed on the Stock Exchange, with anyone being able to purchase and sell them in an open market.
Why does a company issue shares?
The various reasons a company issues shares are as follows:
- Funding Growth: Companies release shares to fund expansion strategies, new projects, and new research and development without being weighed down by debt.
- Debt Settlement: Issuance of shares can relieve a company from the burden of debt liabilities because it raises funds from shareholders instead of loans that result in reduced interest costs.
- Improved Public Profile: It increases brand visibility by attracting potential customers, investors, and partners where once the company goes public through share issuance.
- Liquidity for Founders and Early Investors: It provides liquidity to the founders or early investors by giving them a partial exit while retaining ownership and gaining liquidity.
- Talent Attraction with Equity: Share issuance as compensation to employees attracts and retains talent because employee interest is tied to the company’s success.
Types of shares
The various kinds of stocks represent units of ownership in a company and can be categorized into several categories:
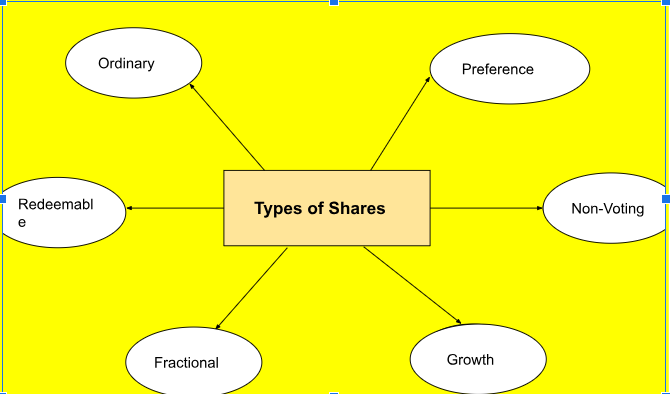
- Ordinary Shares: Holders of these typically have voting rights and may receive dividends, which are paid out from the company’s profits. These types of shares are the most typical.
- Preference Shares: Among the different types of shares, preference shareholders have a higher claim on assets and earnings. They usually receive fixed dividends before any dividends are paid to ordinary shareholders but typically do not have voting rights.
- Redeemable Shares: These types of shares can be bought back by the company at a predetermined price after a certain period.
- Non-voting Shares: These types of shares do not provide the shareholder with voting rights in company decisions but may still offer dividends.
- Fractional Shares: These represent a portion of a whole share, allowing investors to buy less than one full share, making investing more accessible.
- Growth Shares: These are shares in companies expected to grow at an above-average rate compared to their industry or the overall market.
Each type of share offers different rights and benefits, catering to various investor needs and company financing strategies.
Features of equity shares
- Equity shareholders own a part of the business and have voting rights over crucial decisions made within it.
- Shareholders may receive dividends, which will be subject to the profits earned by the company and the dividend policy in place.
- Equity holders claim what’s left after all the debts and liabilities of the business are settled during liquidation.
- Equity shares are readily tradable on the stock exchange, thereby ensuring liquidation for the shareholder.
- Share prices may appreciate, and shareholders can receive potential capital gains.
Types of equity shares
Equity shares can be further divided based on:
- Share capital
- Definition
- Returns
Classification of equity shares based on share capital
Here is a look at the classification of equity shares based on share capital:
- Authorised Share Capital: Every company, in its Memorandum of Associations, is required to prescribe the maximum amount of capital that can be raised by issuing equity shares. The limit, however, can be increased by paying additional fees and after the completion of certain legal procedures.
- Issued Share Capital: This implies the specified portion of the company’s capital, which has been offered to investors through the issuance of equity shares. For example, if the nominal value of one stock is Rs 200 and the company issues 20,000 equity shares, the issued share capital will be Rs 40 lakh.
- Subscribed Share Capital: The portion of the issued capital that has been subscribed by investors is known as subscribed share capital.
- Paid-Up Capital: The amount of money paid by investors for holding the company’s stocks is known as paid-up capital. As investors pay the entire amount at once, subscribed and paid-up capital refers to the same amount.
Classification of equity shares based on definition
Here is a look at the equity share classification based on the definition:
- Bonus Shares: Bonus share definition implies those additional stocks which are issued to existing shareholders free-of-cost, or as a bonus.
- Rights Shares: Right shares mean that a company can provide new shares to its existing shareholders – at a particular price and within a specific period – before being offered for trading in stock markets.
- Sweat Equity Shares: If as an employee of the company, you have made a significant contribution, the company can reward you by issuing sweat equity shares.
- Voting And Non-Voting Shares: Although the majority of shares carry voting rights, the company can make an exception and issue differential or zero voting rights to shareholders.
Classification of equity shares based on returns
Based on returns, here is a look at the types of shares:
- Dividend Shares: A company can choose to pay dividends in the form of issuing new shares on a pro-rata basis.
- Growth Shares: These types of shares are associated with companies that have extraordinary growth rates. While such companies might not provide dividends, the value of their stocks increases rapidly, thereby providing capital gains to investors.
- Value Shares: These types of shares are traded in stock markets at prices lower than their intrinsic value. Investors can expect the prices to appreciate over some time, thus providing them with a better share price.
Features of preference shares
- Preference shareholders get a fixed dividend before equity shareholders.
- In case of liquidation, preference shareholders are paid before equity shareholders.
- In general, preference shareholders do not have voting rights in company decisions.
- Some preference shares can be converted into equity shares after a certain period.
- Companies can repurchase callable preference shares at a pre-set price.
- They carry the attributes of debt with a fixed income along with the features of equity without any entitlement to vote.
- They are risk-free, just like bonds, and involve fixed returns.
Types of preference shares
- Cumulative And Non-Cumulative Preference Shares: In the case of cumulative preference shares, if a particular company doesn’t declare an annual dividend, the benefit is carried forward to the next financial year. Non-cumulative preference shares don’t provide for receiving outstanding dividend benefits.
- Participating/Non-Participating Preference Share: Participating preference shares allow shareholders to receive surplus profits, after payment of dividends by the company. This is over and above the receipt of dividends. Non-participating preference shares carry no such benefits apart from the regular receipt of dividends.
- Convertible/Non-Convertible Preference Shares: Convertible preference shares can be converted into equity shares after meeting the requisite stipulations by the company’s Article of Association (AoA), while non-convertible preference shares carry no such benefits.
- Redeemable/Irredeemable Preference Share: A company can repurchase or claim redeemable preference shares at a fixed price and time. These types of shares are sans any maturity date. Irredeemable preference shares, on the other hand, have no such conditions.
Other types of shares
- Treasury Shares: These are shares a company has repurchased from investors, reducing the number of outstanding shares in the market. Treasury shares do not pay dividends, nor do they have voting rights.
- Class A Shares: They typically offer enhanced voting rights, giving shareholders greater influence over company decisions. They may also have priority in dividend payments.
- Class B Shares: These often carry fewer voting rights than Class A shares and may be issued to retain control within a company. They usually have similar economic benefits.
- Class C Shares: These shares typically come with no voting rights, focusing solely on providing financial returns. They may appeal to investors uninterested in company governance.
Benefits of owning shares
- Potential for Capital Appreciation: Shareholders can benefit from the increase in the stock’s price over time, leading to significant profits upon selling. This potential for growth is one of the primary reasons investors buy many types of shares.
- Dividends: Many companies pay dividends to shareholders, providing a regular income stream. This can be particularly appealing for income-focused investors, as dividends can be reinvested or used as cash flow.
- Voting Rights: Ordinary shareholders typically have the right to vote on key company matters, such as board elections and significant corporate policies, allowing them to influence company direction.
- Diversification: Investing in different types of shares allows individuals to diversify their investment portfolios, spreading risk across various sectors and companies.
- Liquidity: Different types of shares can be easily bought and sold on stock exchanges, providing investors with the flexibility to enter or exit positions as needed. This liquidity is crucial for managing investments effectively.
- Ownership Stake: Owning many types of shares means having a stake in the company’s success. As the company grows and becomes more profitable, shareholders can benefit from that growth through increased share value and dividends.
Risk of owning shares
- Market Volatility: Share prices fluctuate with the overall trend in the market, depending on investor psychology and some macroeconomic indicators. Therefore, the value of a share can drop drastically over time, and short-term predictions based on price are unreliable.
- Economic Factors: Wider economic factors, including inflation, interest rates, and recession, tend to affect the profitability of the company and the value of the stock.
- Company-Specific Risk: Firm-specific issues, including weak management, misdirection, or a decline in earnings, can affect the stock price drastically and lower shareholder wealth.
- Risk of Irregular Dividend: Since shares do not offer fixed income as is the case with debt securities, any alteration in dividend or discontinuing the same hurts investors. In particular, during the time of economic downturn, when firms may even eliminate the dividend, it certainly does have a negative impact on shareholders who rely on dividend flow for returns.
Conclusion
Investing in shares can prove to be a great source of long-term wealth generation for any individual investor. Stocks provide you with a variety of sectors and industries to choose from, helping you diversify your portfolio and mitigate your risks. Always remember to narrow down on trusted and reliable financial partners to open your Demat account and trading account, like IIFL Capital Services Limited.

![]() IIFL Customer Care Number
IIFL Customer Care Number ![]() IIFL Capital Services Support WhatsApp Number
IIFL Capital Services Support WhatsApp Number