Table of Content
During the IPO application process, a company can change itself from a privately-held entity to a publicly-traded entity through the process of Initial Public Offering (IPO). Typically, companies offer IPO to raise money and get access to liquidity by offering their stocks/shares to the public. Companies have to abide by the IPO process in India, as stipulated by stock exchanges, before their shares are eligible to be publicly traded. This process is often complicated and long-drawn.
You Might Also Like, What is IPO?
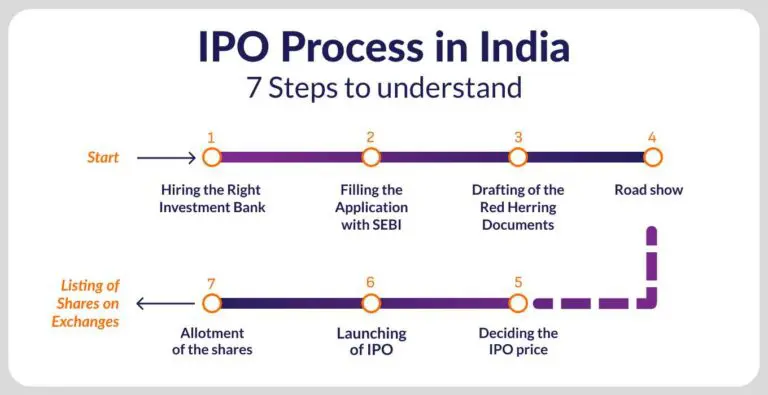
To start the initial public offering process, the company will take the help of financial experts, like investment banks. The underwriters assure the company about the capital being raised and act as intermediaries between the company and its investors. The experts will also study the crucial financial parameters of the company and sign an underwriting agreement. The underwriting agreement will usually have the following components:
This IPO step involves the preparation of a registration statement along with the draft prospectus, also known as Red Herring Prospectus (RHP). Submission of RHP is mandatory, as per the Companies Act. This document comprises all the compulsory disclosures as per the SEBI and Companies Act. Here’s a look at the key components of RHP:
This document has to be submitted to the registrar of companies, three days before the offer opens to the public for bidding. Alongside, the submitted registration statement has to be compliant with the SEC rules. Post-submission, the company can make an application for an IPO to SEBI.
Market regulator, SEBI then verifies the disclosure of facts by the company. If the application is approved, the company can announce a date for its IPO.
The company now has to make an application to the stock exchange for floating its initial issue.
Before an IPO opens to the public, the company endeavors to create a buzz in the market by roadshows. Over a period of two weeks, the executives and staff of the company will advertise the impending IPO across the country. This is basically a marketing and advertising tactic to attract potential investors. The key highlights of the company are shared with various people, including business analysts and fund managers. The executives adopt various user-friendly measures, like Question and Answer sessions, multimedia presentations, group meetings, online virtual roadshows, and so on.
The company can now initiate pricing of IPO either through Fixed Price IPO or by Book Binding Offering. In the case of Fixed Price Offering, the price of the company’s stocks is announced in advance. In the event of Book Binding Offering, a price range of 20% is announced, following which investors can place their bids within the price bracket. For the bidding process, the investors have to place their bids as per the company’s quoted Lot price, which is the minimum number of shares to be purchased. Alongside, the company also provides for IPO Floor Price, which is the minimum bid price and IPO Cap Price, which is the highest bidding price. The booking is typically open from three to five working days and investors can avail the opportunity of revising their bids within the stipulated time. After completion of the bidding process, the company will determine the Cut-Off price, which is the final price at which the issue will be sold.
Once the IPO price is finalised, the company along with the underwriters will determine the number of shares to be allotted to each investor. In the case of over-subscription, partial allotments will be made. The IPO stocks are usually allotted to the bidders within 10 working days of the last bidding date.
Also Read, IPO Allotment Process
Here is a list of IPO filing requirements:
There might be fewer or more documents required as per the nature of the IPO.
Here is the timeline of the IPO presented in a tabular format:
| Stage | Activity | Approximate Timeframe |
| Planning & Preparation | Appoint merchant bankers, legal advisors | 2–4 weeks |
| Due Diligence & Drafting | Prepare Draft Red Herring Prospectus (DRHP) | 3–6 weeks |
| Filing with SEBI | Submit DRHP to SEBI for review | Day 0 |
| SEBI Review & Comments | SEBI reviews and gives observations | 4–6 weeks |
| RHP Finalization | Update RHP and file with Registrar of Companies | 1–2 weeks after SEBI approval |
| Roadshows & Marketing | Promote IPO to investors | 1–2 weeks |
| IPO Opens | Investors apply for shares | 3–5 days |
| IPO Closes | Last day to submit bids | End of IPO window |
| Basis of Allotment | Shares allotted to applicants | Within 6 working days of close |
| Listing on the Stock Exchange | Shares listed and begin trading | 6–10 working days after close |
Now that you know the IPO process steps and its importance, you can make informed decisions to invest in IPOs. Also, have a look at Indiainfoline upcoming IPO calendar to aid your understanding on IPO. To make prudent investment decisions, you will be invariably required to do a lot of legwork.
This includes selecting a trusted and reliable financial partner. You must select a stockbroking firm providing multiple benefits such as smooth trading platforms, an all-in-one account to trade in all investment options, zero Demat account opening and AMC charges, award-winning research, and so on. These help with the IPO subscription procedure for investors.
An IPO, or Initial Public Offering, is when a private company decides to offer its shares to the public for the first time. This transition allows the company to raise capital from investors and become publicly traded on a stock exchange.
An IPO involves appointing underwriters, filing regulatory documents, determining a share price, and offering shares to the public. After the IPO, the company is listed on a stock exchange, allowing investors to buy and sell its shares.
An IPO can be profitable, offering early investors and shareholders a chance to benefit from price appreciation. However, returns depend on market conditions, company performance, and investor sentiment.
Investing in an IPO can be rewarding if the company has strong growth potential. However, it carries risks like volatility and uncertainty, requiring careful analysis of the company’s fundamentals and industry trends.
IPO shares can be sold through a trading account once the company is listed on a stock exchange. Investors can sell their shares at market price or set a preferred selling price.
![]() IIFL Customer Care Number
IIFL Customer Care Number
(Gold/NCD/NBFC/Insurance/NPS)
1860-267-3000 / 7039-050-000
![]() IIFL Capital Services Support WhatsApp Number
IIFL Capital Services Support WhatsApp Number
+91 9892691696
IIFL Capital Services Limited - Stock Broker SEBI Regn. No: INZ000164132, PMS SEBI Regn. No: INP000002213,IA SEBI Regn. No: INA000000623, SEBI RA Regn. No: INH000000248, DP SEBI Reg. No. IN-DP-185-2016, BSE Enlistment Number (RA): 5016
ARN NO : 47791 (AMFI Registered Mutual Fund & Specialized Investment Fund Distributor), PFRDA Reg. No. PoP 20092018

This Certificate Demonstrates That IIFL As An Organization Has Defined And Put In Place Best-Practice Information Security Processes.