Table of Content
In the Indian options market, it is the index options that are a lot more popular and liquid. Just as a stock is an option on a stock, the index option is an option on a well-accepted index like the Nifty, Sensex, Bank Nifty, etc. What are index options and how do they work? Apart from the index options definition, let us also look at what is index options conceptually. Here is a quick take on what are index options, the types of index options, and how and when to apply the same.
Index Options are the derivative instrument, which means their value is derived from the movements in the underlying index. In India, there are popular indexes like the Sensex, Nifty, Bank Nifty, Nifty Financial Services. Supposed you want to take a view on these indices rather than on individual stocks, you can use index options. You can also use index options to protect your portfolio by using contrary index options as a hedge.
Normally, index options are available where the futures are already available so there is a benchmark for option pricing. Then the lot sizes, strike prices, and different expiry periods are determined for the index options and once they are standardized, they are ready and all set to trade. Unlike futures which is a kind of discrete product where either the buyer gains or the seller gains, the trader in index options is a lot more asymmetric in nature. That means; the buyer of the index options only pays the premium and that also represents their maximum possible loss.
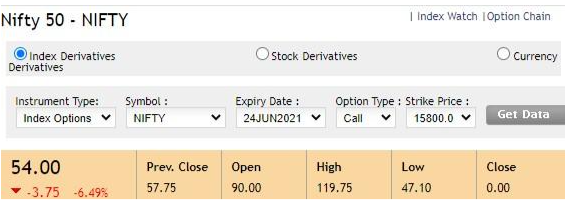
Data Source: NSE
The above is the Nifty call options contract on a strike price of Rs.15,800 when the nifty spot value is at 15,772 in the NSE. This is a right to buy Nifty at an exercise price of Rs.15,800 without the obligation to buy. However, to get this right without the obligation is a privilege you need to pay a price. Currently, the price you need to pay for this right is Rs.54 and the price keeps constantly changing depending on the view on the Nifty future movement.
What happens if you buy the Nifty 15,800 call option at Rs.54? Nifty has a minimum lot of 75 shares of Nifty so that is the bare minimum you need to buy. So, buying one lot of Nifty 15,800 call option (right to buy at 15,800) will cost you Rs.4,050. Remember that the options contract will expire on the last Thursday of June which is 24 June. So, you have just 2 days left to close the position at a profit. In the meanwhile, if the Nifty falls sharply, you may not get anything and lose the entire Rs.4,050.
If the Nifty goes up to 15,810 on Wednesday and the Nifty option goes up to Rs.70, then you book a profit of Rs.1,200 (75×16) on the trade and walk out with a profit. Either way, your maximum loss on this index options trade can never be more than Rs.4,050. Of course, when you add up the brokerage and statutory charges, you would find that the minimum loss is higher than that but that is the whole idea.
Let us quickly go one step ahead and look at the types of index options. The index options classification can be done in 3 ways as under.
Index options trading is buying or selling options on a stock market index. Traders use these options to speculate on market trends, hedge against portfolio risks, or make strategic trades. Call options give the right to profit from an index’s increase, while put options profit when it falls.
The contracts are cash-settled at expiration based on the closing value of the index. Index options allow for flexibility because traders can use different strike prices and expiries to match their market outlook. This type of trading is popular because it has low capital requirements and effectively mitigates systematic risks.
India stock exchanges, including the NSE, host index options trading. Traders go for an index such as the Nifty 50 and choose an options contract depending on their view of the market. They can buy a call option for a bullish outlook or a put option for a bearish one. Contracts have standardised specifications, including expiry dates and strike prices.
Margins are required for selling options, while buyers pay a premium. At expiry, the contracts are cash-settled based on the index’s closing value. This structured process ensures transparency, regulatory compliance, and efficient trade execution.
Factors influencing the valuation of index options include the current level of the index, strike price, time to expiry, volatility, interest rates, and dividends. Theoretical values are usually calculated using pricing models such as the Black-Scholes formula. The intrinsic value is simply the difference between the current index level and the strike price, while the time value represents the remaining lifespan of the option and its possibility to be exercised before its expiration.
Volatility, especially implied volatility, is a very important factor in valuation because it reflects the expected price movements. The correct valuation helps traders make the right decisions and manage risk in their portfolios.
Index options strategies are designed to help traders maximise returns or minimise risks depending on their market outlook.
Normally, all options are valued based on a formula called the Black and Scholes method which helps you to calculate the intrinsic value of the call and put option. The formulas are available stored in the NSE website and also in the trading software so there is not much of number crunching you need to do. Just put the data and you get the output.
Index options are the most volatile as they are highly liquid and also popular among large traders, proprietary desks and institutions. The volatility of index options is normally calculated with a popular measure called the implied volatility or IV.
The choice between stock and index options depends on your trading goals. Stock options offer specific company exposure, while index options provide broader market exposure. Index options are generally less risky as they reflect market trends, while stock options can be more volatile due to individual company performance.
To trade index options, you can buy call options if you expect the market to rise or put options if you anticipate a decline. Traders can also use strategies like spreads, straddles, and strangles to manage risk and profit from market volatility or stable conditions.
Index options do not represent shares of a company but rather a portion of a stock market index, such as the Nifty 50 or Sensex. The value of the option is derived from the index’s movement. Typically, index options are cash-settled based on the index’s value, not shares.
![]() IIFL Customer Care Number
IIFL Customer Care Number
(Gold/NCD/NBFC/Insurance/NPS)
1860-267-3000 / 7039-050-000
![]() IIFL Capital Services Support WhatsApp Number
IIFL Capital Services Support WhatsApp Number
+91 9892691696
IIFL Capital Services Limited - Stock Broker SEBI Regn. No: INZ000164132, PMS SEBI Regn. No: INP000002213,IA SEBI Regn. No: INA000000623, SEBI RA Regn. No: INH000000248, DP SEBI Reg. No. IN-DP-185-2016, BSE Enlistment Number (RA): 5016
ARN NO : 47791 (AMFI Registered Mutual Fund & Specialized Investment Fund Distributor), PFRDA Reg. No. PoP 20092018

This Certificate Demonstrates That IIFL As An Organization Has Defined And Put In Place Best-Practice Information Security Processes.